The rear end of a pickup truck, also known as the truck bed, is an essential feature that distinguishes it from other vehicles. Designed to carry cargo, the pickup truck’s rear end serves as a versatile space for transporting goods, equipment, and materials. With its sturdy construction and ample capacity, the rear end of a pickup truck plays a crucial role in enabling businesses, contractors, and individuals to efficiently transport and deliver various items. Whether it’s hauling construction supplies, moving furniture, or transporting recreational gear, the rear end of a pickup truck is a practical and functional component that enhances the truck’s utility and versatility. Understanding the purpose and potential of the rear end of a pickup truck is vital for both truck owners and those in need of reliable transportation solutions. The rear end of a pickup truck is composed of several components that play important roles in the overall functionality and design of the vehicle. From the rear bumper to the rear window, each part serves a specific purpose to ensure the safety and efficiency of the truck. In this comprehensive article, we will explore each section in detail, providing insight into the rear bumper, cargo bed, tailgate, rear suspension, rear lights, hitch and towing capabilities, rear axle, rear-wheel drive, rear fender, rearview mirror and camera, rear steer, and finally, the rear window.
Rear Bumper
The rear bumper of a pickup truck serves as a protective barrier between the vehicle’s body and any potential impact. While its primary function is to absorb the shock of a collision and minimize damage to the pickup truck, it also contributes to the overall aesthetics of the vehicle. Rear bumpers are typically made from durable materials such as steel or aluminum, and their design varies depending on the make and model of the truck. Some rear bumpers also incorporate features such as tow hooks or receiver hitches, adding versatility to the pickup truck’s capabilities.
Cargo Bed
The cargo bed, also known as the truck bed, is the open space located at the rear of the pickup truck. It is designed to carry and transport various types of cargo, ranging from equipment and tools to large materials or even recreational items such as bicycles and ATVs. Cargo beds come in different sizes and configurations, with options such as short beds, long beds, or in some cases, even flatbeds. They are usually made from sturdy materials like steel or aluminum to withstand heavy loads and endure harsh environments.
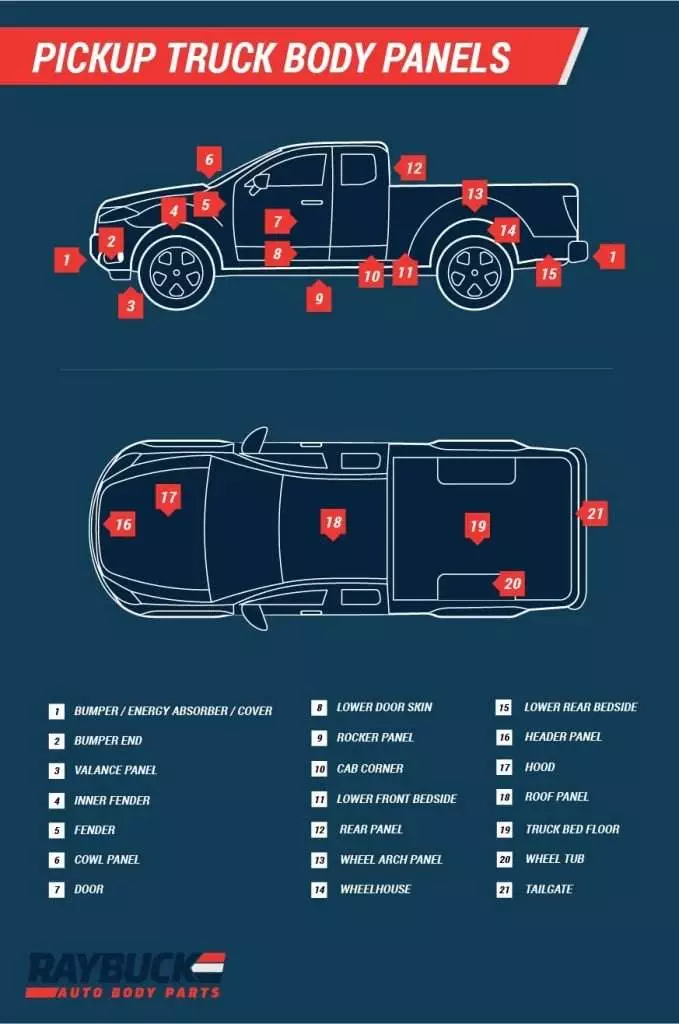
This image is property of raybuck.com.
Tailgate
The tailgate is the hinged door located at the rear end of the cargo bed. It serves as an access point for loading and unloading items into the bed, while also acting as a barrier to prevent cargo from falling out while the truck is in motion. The tailgate can be opened and closed, providing flexibility for different types of loading and unloading scenarios. Some pickup trucks come with tailgates that offer additional features, such as built-in steps or the ability to be converted into a workbench or seating area. The tailgate design often reflects the brand’s identity and can be customized by truck owners for personalization or utility.
Rear Suspension
The rear suspension system plays a crucial role in providing a comfortable ride and maintaining the stability of the pickup truck, especially when carrying heavy loads. There are various types of rear suspension systems commonly found in pickup trucks, including leaf springs, coil springs, and air suspension.
Leaf Springs
Leaf springs consist of multiple layers of curved metal strips, called leaves, that are stacked on top of each other and secured with a center bolt. They are known for their durability and ability to handle substantial weight loads, making them a popular choice for commercial and heavy-duty trucks. Leaf springs provide a firm and stable ride, but they can be susceptible to a harsher driving experience on uneven terrain.
Coil Springs
Coil springs, as the name suggests, are coiled metal springs that compress and expand to absorb shocks and bumps. They offer a smoother ride compared to leaf springs and can be found in a wider range of pickup trucks, including both light-duty and heavy-duty models. Coil springs are often combined with shock absorbers to enhance the overall suspension performance, providing a balance between comfort and load-carrying capacity.
Air Suspension
Air suspension systems utilize compressed air to support the weight of the pickup truck, providing a highly adjustable and responsive suspension setup. This type of suspension can be electronically controlled to automatically adjust the ride height depending on the load or driving conditions. Air suspension offers improved comfort and handling, making it a popular choice for luxury or off-road trucks. However, it is generally more complex and expensive to maintain compared to traditional spring-based suspensions.
This image is property of qph.cf2.quoracdn.net.
Rear Lights
The rear lights of a pickup truck are essential for ensuring visibility and safety on the road. Three main types of rear lights are commonly found on pickup trucks: brake lights, turn signals, and reverse lights.
Brake Lights
The brake lights, typically positioned near the outer edges of the rear end, illuminate when the driver applies the brakes. They serve as a warning to other drivers behind the pickup truck, indicating that it is slowing down or coming to a stop. Brake lights are crucial for preventing rear-end collisions, especially in low-visibility situations or heavy traffic.
Turn Signals
Turn signals, also known as indicators or blinkers, are located on both sides of the rear end. When activated by the driver, they emit a blinking signal to indicate their intention to make a turn or change lanes. Turn signals play a vital role in communicating the driver’s actions to other motorists, enhancing overall road safety.
Reverse Lights
Reverse lights, situated at the rear end and often housed within the tailgate or rear bumper, illuminate when the driver shifts the transmission into reverse gear. These lights provide additional illumination to the area behind the truck, allowing the driver to see and maneuver more effectively when backing up. Reverse lights are particularly important in low-light conditions or crowded areas, minimizing the risk of collisions and ensuring pedestrian safety.
Hitch and Towing
Many pickup truck owners utilize their vehicles for towing purposes, whether it be hauling trailers, campers, or boats. The rear end of a pickup truck is equipped with several components that enable safe and efficient towing.
Hitch Receiver
The hitch receiver is a crucial component located at the rear of the truck, providing a secure attachment point for towing trailers or other equipment. It consists of a square or rectangular opening that accepts a compatible hitch, commonly referred to as a receiver hitch. Hitch receivers come in various sizes and weight ratings, allowing truck owners to select the appropriate one based on their towing needs. They are typically made from heavy-duty materials such as steel and require professional installation to ensure structural integrity and safety.
Towing Capacity
The towing capacity refers to the maximum weight that a pickup truck can safely tow. It is determined by various factors, including the truck’s engine power, transmission, rear axle ratio, suspension system, and braking capacity. Manufacturers specify the towing capacity for each specific truck model, and it is essential for truck owners to adhere to these guidelines to prevent vehicle damage or accidents. It is important to note that exceeding the towing capacity can put undue stress on the truck’s components, such as the engine, transmission, and brakes, compromising safety and potentially leading to costly repairs.
Trailer Wiring
To safely tow trailers or other equipment, pickup trucks are equipped with trailer wiring systems. These systems allow electrical connections between the truck and the trailer, enabling trailer brake lights, turn signals, and other electronic components to function properly. Pickup trucks are typically equipped with a standard trailer wiring harness, and additional components such as trailer brake controllers may be required for larger or specialized trailers. Ensuring proper installation and maintenance of the trailer wiring system is crucial for safe towing operations.

This image is property of static.foxdealer.com.
Rear Axle
The rear axle is a vital component of the pickup truck’s drivetrain, responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the rear wheels. It consists of several key elements, including the differential, axle shafts, and wheel hubs.
Differential
The differential is housed within the rear axle and is responsible for distributing power from the engine to the rear wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds during turns. This enables smooth and stable cornering performance, as the outer wheel can rotate at a faster speed than the inner wheel. The differential also plays a critical role in transferring torque to the rear wheels evenly, depending on traction conditions. In certain pickup trucks, differential lock systems may be available, providing enhanced off-road capability by mechanically connecting the rear wheels for increased traction.
Axle Shaft
Axle shafts, also known as half-shafts or drive shafts, transmit torque from the differential to the rear wheels, allowing them to rotate and propel the pickup truck forward. These shafts are typically made from durable materials such as hardened steel to withstand the high levels of torque and rotational forces exerted during acceleration and heavy-duty operations. Axle shafts are equipped with constant velocity (CV) joints at each end, which allow for smooth power transmission and accommodate the up-and-down movement of the suspension as the wheels articulate.
Wheel Hub
The wheel hub, located at the center of each rear wheel, provides the mounting point for the wheel itself. It supports the weight of the pickup truck and enables the wheels to rotate freely. Wheel hubs are equipped with bearings that allow for smooth rotation and minimize friction. Proper maintenance and lubrication of the wheel hubs are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Rear-Wheel Drive
Rear-wheel drive (RWD) is a common drivetrain configuration found in pickup trucks, as well as many other vehicles. Unlike front-wheel drive (FWD) or all-wheel drive (AWD), where the power is sent to the front wheels or distributed among all four wheels, RWD directs the engine’s power exclusively to the rear wheels. This configuration offers several advantages, including improved weight distribution, enhanced traction under heavy loads, and better handling characteristics. RWD pickup trucks are generally favored by truck enthusiasts and those who require towing or off-road capabilities.
Drive Shaft
In rear-wheel drive pickup trucks, the power from the engine is transmitted to the rear axle through a component called the driveshaft. The driveshaft is a long, tubular shaft that connects the transmission or transfer case to the differential, allowing for the smooth transfer of rotational force. It consists of a series of U-joints and may have a center support bearing to maintain stability and reduce vibrations. The driveshaft’s length and construction vary depending on the truck’s size, engine placement, and rear axle configuration.
This image is property of qph.cf2.quoracdn.net.
Rear Fender
The rear fender, also known as the quarter panel, is a structural component that covers the rear wheels of the truck, enclosing the wheel well area. It serves both functional and aesthetic purposes, providing protection from road debris and enhancing the overall appearance of the pickup truck. Rear fenders can be made from different materials, such as steel or fiberglass, and their design may include features like fender flares for a more aggressive and robust look.
Wheel Well
The wheel well is the space surrounding the rear wheels within the rear fender. It accommodates the vertical movement of the suspension as the wheels travel over bumps and provides clearance for tire rotation. The design and size of the wheel well can vary depending on the truck’s suspension configuration, tire size, and intended use. Some pickup trucks may have larger wheel wells to accommodate off-road tires or aftermarket suspension modifications.
Fender Flares
Fender flares are extensions or bulges added to the rear fender to increase wheel coverage and protect the truck’s body from mud, rocks, or other debris kicked up by the tires. They enhance the truck’s off-road capability by allowing for the fitment of larger tires without compromising clearance and offer a more rugged and aggressive appearance. Fender flares come in a variety of styles and materials, ranging from subtle and factory-matching to bold and aftermarket options.
Rearview Mirror and Camera
The rearview mirror and backup camera are two features that enhance the driver’s visibility and aid in maneuvering the truck in rearward directions.
Rearview Mirror
The rearview mirror is an essential safety feature that provides the driver with a clear view of the road behind the vehicle. It is typically mounted inside the cabin and positioned to reflect the view through the rear windshield. Rearview mirrors may vary in size and design, offering features such as auto-dimming capabilities, integrated compasses, or garage door opener controls. They play a crucial role in allowing the driver to monitor the traffic situation and make informed decisions while driving in reverse or changing lanes.
Backup Camera
Backup cameras, also known as rearview cameras or rear-facing cameras, have become increasingly common in modern pickup trucks. These cameras are typically mounted on the rear end, either integrated into the tailgate handle or positioned near the license plate. When engaged, the backup camera provides a live video feed to the infotainment screen or rearview mirror, allowing the driver to view the area behind the truck. This feature aids in parking, maneuvering in tight spaces, and reducing the blind spot when reversing. Backup cameras help minimize the risk of accidents and are particularly useful when towing trailers or in situations where visibility may be limited.

This image is property of www.vanpeltsales.com.
Rear Steer
Rear steer refers to the capability of a pickup truck to turn or steer the rear wheels in addition to the front wheels. While conventional pickup trucks typically have fixed rear wheels, some models feature rear steer systems for enhanced maneuverability and stability.
Four-Wheel Steering
Four-wheel steering, also known as all-wheel steering or quadra-steer, enables the rear wheels to turn in the same direction as the front wheels, reducing the turning radius. This feature improves overall maneuverability, particularly in tight spaces or when navigating crowded urban environments. By minimizing the truck’s turning radius, four-wheel steering allows for easier parking and enhances the truck’s agility. It can also improve stability during high-speed maneuvers, as the rear wheels can countersteer to help maintain control.
Rear Wheel Steering
Rear wheel steering, unlike four-wheel steering, enables the rear wheels to turn in the opposite direction of the front wheels. This feature is typically found in off-road or heavy-duty pickup trucks, where enhanced stability and control are important. Rear wheel steering helps with reducing oversteer, improving cornering stability, and enhancing traction in challenging terrains. By allowing the rear wheels to track a different path than the front wheels, rear wheel steering offers improved maneuverability, especially in off-road situations where precise navigation is necessary.
Rear Window
The rear window of a pickup truck provides visibility to the rear of the vehicle and contributes to overall safety and convenience features. Depending on the pickup truck’s design and configuration, there are different types of rear windows commonly found.
Rear Windshield
The rear windshield, also known as the rear glass or backlite, is the large, often curved piece of glass located at the back of the pickup truck’s cab. It provides a clear view of the area behind the truck and allows natural light to enter the cabin. Rear windshields are typically made from laminated safety glass, which helps prevent shattering and provides additional support to the truck’s structure. Some rear windshields may also feature defroster elements or embedded antennas for improved functionality.
Slider Window
Slider windows, also referred to as sliding rear windows or rear sliding windows, are an optional feature found in many pickup trucks. These windows are typically installed at the rear section of the truck’s cab and can be manually opened or closed horizontally. Slider windows provide ventilation to the cabin, allowing for air circulation when the main windows are closed. They also offer an additional rearward view and can be particularly useful for truck owners who frequently transport pets or require extended ventilation.
In conclusion, the rear end of a pickup truck is composed of various components that contribute to the vehicle’s functionality, safety, and design. From the rear bumper, cargo bed, and tailgate to rear suspension, lights, and hitch/towing capabilities, each section plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and efficient driving experience. Additionally, the rear axle, rear-wheel drive system, rear fenders, rearview mirror and camera, rear steer systems, and rear windows all contribute to the overall performance and functionality of the pickup truck. With a thorough understanding of each component, truck owners and enthusiasts can appreciate the intricate engineering behind the rear end of a pickup truck and make informed decisions when choosing the right vehicle for their needs.



